Support our educational content for free when you purchase through links on our site. Learn more
What is Better: Filament or Resin? [2024]
Have you ever wondered which is better for 3D printing: filament or resin? It’s a common question among 3D printing enthusiasts, and the answer depends on various factors. In this article, we will delve into the world of filament and resin 3D printing, comparing their features, benefits, and drawbacks. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which option is best suited for your needs.
Quick Answer
When it comes to choosing between filament and resin for 3D printing, there is no definitive answer. It ultimately depends on your specific requirements and preferences. Filament 3D printing offers versatility, accessibility, and durability, making it a popular choice for many. On the other hand, resin 3D printing provides high resolution, intricate details, and smoother finishes, making it ideal for applications that require precision and aesthetics. Consider factors such as project requirements, desired print quality, printing speed, and budget to make an informed decision.
CHECK PRICE on:
Quick Tips and Facts
Before we dive deeper into the comparison, here are some quick tips and facts to keep in mind:
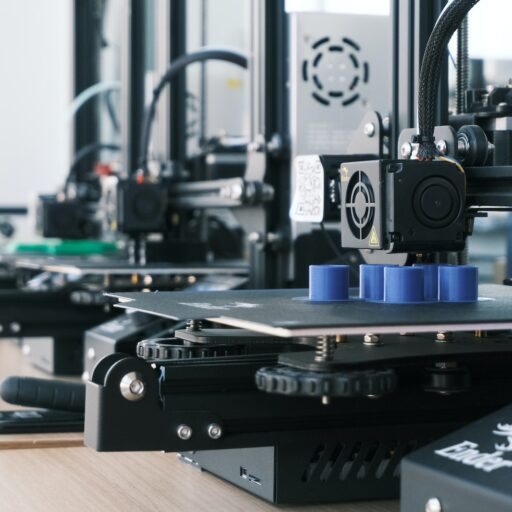
- Filament 3D printing uses plastic filament melted and extruded through a hot nozzle, while resin 3D printing uses liquid resin material cured by UV light to create objects.
- Filament printing is generally quicker and produces prints with higher tensile strength, while resin printing takes longer but produces higher quality, detailed prints with smoother finishes.
- Filament 3D printers are more versatile and accessible, with a wider range of materials and larger build volumes. Resin 3D printers offer higher resolution and are better suited for intricate designs.
- Filament prints may have visible layer lines, while resin prints have smoother surfaces due to higher resolution and smoother finishes.
- Filament 3D printing is more cost-effective in terms of materials, while resin 3D printing can be more expensive due to the cost of resin and post-processing requirements.
- Filament prints are generally more durable, while resin prints can be brittle and have limited shelf-life.
Now that we have a quick overview, let’s explore the world of filament and resin 3D printing in more detail.
Background: Filament and Resin 3D Printing

What is Filament 3D Printing?
Filament 3D printing, also known as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), is one of the most common and accessible methods of 3D printing. It involves the use of a continuous filament of thermoplastic material, such as PLA or ABS, which is melted and extruded through a hot nozzle. The melted filament is then deposited layer by layer to create a three-dimensional object.
Filament 3D printers are widely available and come in various sizes and price ranges, making them suitable for both beginners and professionals. They offer a wide range of materials, including different types of plastics, composites, and even flexible filaments. This versatility allows for the creation of functional prototypes, mechanical parts, artistic models, and more.
What is Resin 3D Printing?
Resin 3D printing, also known as Stereolithography (SLA) or Digital Light Processing (DLP), is a different approach to 3D printing. Instead of using a filament, resin 3D printing utilizes a liquid photopolymer resin that is selectively cured into a solid shape layer by layer. This is achieved by exposing the liquid resin to a light source, such as a laser or a projector, which triggers a chemical reaction and solidifies the resin.
Resin 3D printers offer exceptional print quality, with high resolution and intricate details. They are commonly used in industries such as jewelry, dentistry, and prototyping, where precision and aesthetics are crucial. Resin prints have smoother surfaces compared to filament prints, making them ideal for applications that require a high level of detail and a polished finish.
1. Filament 3D Printing: Features, Benefits, and Drawbacks
1.1 Versatility and Accessibility
Filament 3D printing is known for its versatility and accessibility. With a wide range of materials available, including PLA, ABS, PETG, and more, filament printers can cater to various project requirements. Whether you need a strong and durable part or a flexible and heat-resistant prototype, there is a filament material suitable for the job.
Filament 3D printers are also widely available and come in different sizes and price ranges. From entry-level models for beginners to professional-grade machines for advanced users, there is a filament printer to fit every budget and skill level. This accessibility makes filament 3D printing a popular choice among hobbyists, educators, and small businesses.
1.2 Build Volume and Durability
Another advantage of filament 3D printing is the ability to print large objects due to the larger build volumes offered by most filament printers. This makes it suitable for creating functional prototypes, architectural models, and other projects that require a significant size.
Filament prints are generally more durable compared to resin prints. The layer-by-layer deposition of molten plastic creates a strong bond between the layers, resulting in robust and sturdy objects. This durability makes filament prints suitable for functional parts, mechanical components, and other applications that require strength and reliability.
1.3 Layer Lines and Support Structures
One drawback of filament 3D printing is the visibility of layer lines on the printed objects. Since the filament is deposited layer by layer, the individual layers can be noticeable, especially on larger prints. However, this can be mitigated by using finer layer heights and post-processing techniques such as sanding and painting.
Filament prints may also require support structures for overhangs and complex geometries. These support structures are printed alongside the main object and need to be removed manually after printing. While support structures are necessary for achieving certain designs, they can add complexity and post-processing time to the printing process.
CHECK PRICE on:
2. Resin 3D Printing: Features, Benefits, and Drawbacks
2.1 High Resolution and Intricate Details
One of the main advantages of resin 3D printing is its ability to produce highly detailed and precise prints. The liquid resin allows for finer details and smoother surfaces compared to filament prints. This makes resin 3D printing ideal for applications that require intricate designs, such as jewelry, miniatures, and figurines.
Resin prints also have a higher resolution, meaning they can achieve finer layer heights and produce more accurate models. This level of detail is especially important for industries like dentistry and engineering, where precision is crucial.
2.2 Water-Resistant Prints and Unaffected Surface Quality
Resin prints have the advantage of being water-resistant, thanks to the nature of the cured resin material. This makes them suitable for applications that may come into contact with liquids or require water-tightness, such as custom containers, dental models, or prototypes for water-related products.
Additionally, resin prints maintain their surface quality even after post-processing. Unlike filament prints, which may require sanding and painting to achieve a smooth finish, resin prints come out of the printer with a polished appearance. This saves time and effort in post-processing, making resin 3D printing more efficient for certain applications.
2.3 Limited Printing Size and Post-Processing Requirements
One limitation of resin 3D printing is the limited printing size compared to filament printers. Most resin printers have smaller build volumes, which can restrict the size of the objects that can be printed. This may not be an issue for smaller-scale projects, but it can be a drawback for larger prototypes or functional parts.
Resin prints also require post-processing to remove excess resin and cure the prints fully. This involves rinsing the prints in a solvent, such as isopropyl alcohol, and then curing them under UV light. While this post-processing step is necessary to achieve the final desired properties of the resin prints, it can be time-consuming and messy.
CHECK PRICE on:
3. Is a Resin or Filament Printer Better? [FAQ]
![3. Is a Resin or Filament Printer Better? [FAQ] by Best 3D Printer a close up of a blue and purple structure](https://www.best3dprinter.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/54/2024/02/photo-1643780668909-580822430155cropentropycstinysrgbfitmaxfmjpgixidM3w0NDMxOTh8MHwxfHNlYXJjaHw3fHwzZCUyMHByaW50ZXIlMjBmaWxhbWVudCUyMHZzJTIwcmVzaW4lMjBjb21wYXJpc29ufGVufDB8fHx8MTcwNjgwMTI3NXwwixlibrb-4.0.jpg)
3.1 Is a resin or filament printer better?
The choice between a resin and filament printer depends on your specific requirements and preferences. If you prioritize versatility, accessibility, and durability, a filament printer may be the better option for you. On the other hand, if you need high resolution, intricate details, and smoother finishes, a resin printer would be more suitable. Consider factors such as project requirements, desired print quality, printing speed, and budget to make an informed decision.
3.2 Is resin or filament better for cosplay?
When it comes to cosplay, both resin and filament can be used depending on the specific needs of the costume or prop. Filament prints are generally more durable and can withstand rough handling, making them suitable for larger props or wearable parts. Resin prints, on the other hand, offer higher resolution and smoother finishes, which can be beneficial for intricate details and smaller accessories. Consider the requirements of your cosplay project and choose the printing method that best meets those needs.
3.3 Is PLA better quality than resin?
PLA and resin are different materials used in 3D printing, and their quality depends on the specific application. PLA is a type of filament material known for its ease of use, low cost, and biodegradability. It is suitable for a wide range of applications, including prototypes, artistic models, and functional parts. Resin, on the other hand, offers higher resolution and smoother finishes, making it ideal for applications that require intricate details and aesthetics. The choice between PLA and resin depends on the specific requirements of your project.
3.4 What are the disadvantages of resin 3D printing?
Resin 3D printing has some disadvantages that you should consider before choosing this method. These include:
- Limited printing size: Resin printers typically have smaller build volumes compared to filament printers, which can restrict the size of the objects that can be printed.
- Toxic fumes: The liquid resin used in resin printing can emit strong odors and potentially harmful fumes during the printing and post-processing stages. It is important to use resin printers in a well-ventilated area or with proper air filtration systems.
- Messy and time-consuming post-processing: Resin prints require post-processing steps such as rinsing in a solvent and curing under UV light. This can be messy and time-consuming compared to filament prints, which usually require minimal post-processing.
- Limited shelf-life: Resin materials have a limited shelf-life, meaning they can degrade over time and may not produce the same quality prints if stored for an extended period.
Consider these drawbacks when deciding whether resin 3D printing is the right choice for your projects.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the choice between filament and resin 3D printing depends on your specific requirements and preferences. Filament 3D printing offers versatility, accessibility, and durability, making it a popular choice for many applications. Resin 3D printing provides high resolution, intricate details, and smoother finishes, making it ideal for projects that require precision and aesthetics.
Consider factors such as project requirements, desired print quality, printing speed, and budget when making your decision. If you prioritize versatility and durability, a filament printer may be the better option. If you need high resolution and smoother finishes, a resin printer would be more suitable.
Remember to check out our 3D Printer Reviews and 3D Printer Brands categories for more information on the best 3D printers available.
Recommended Links
- Which is Better: FDM or Resin 3D Printing? 2023
- 3D Printer Reviews
- 3D Printer Brands
- 3D Printers for Small Businesses
- 3D Printing Industry News