Support our educational content for free when you purchase through links on our site. Learn more
[2023] What is a 3D Printer and How Does It Work?

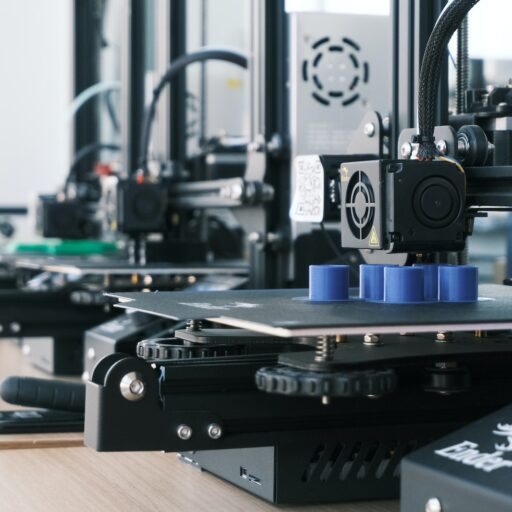
Welcome to Best 3D Printer™, the ultimate resource for all things 3D printing! In this comprehensive guide, we will answer the burning question: What is a 3D printer and how does it work? Whether you're a beginner or an enthusiast looking to expand your knowledge, we've got you covered. So let's dive in and explore the fascinating world of 3D printing!
Table of Contents
- Quick Answer
- Quick Tips and Facts
- How Does 3D Printing Work?
- Types of 3D Printers
- What Can You 3D Print?
- How Do 3D Printers Work?
- The 3D Printing Process
- How Much Do 3D Printers Cost?
- 3D Printing Examples
- 3D Printing Uses
- Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing
- FAQ
- Conclusion
- Useful Links
- Reference Links
Quick Answer
A 3D printer is a revolutionary device that creates physical objects by layering materials based on a digital design. It works by melting or curing a material, such as plastic or resin, and precisely depositing it layer by layer to build a three-dimensional object. 3D printing technology has rapidly advanced in recent years, enabling a wide range of applications across industries.
Quick Tips and Facts
- 3D printing is also known as additive manufacturing, as it adds material to build objects instead of subtracting material like traditional manufacturing processes.
- The first 3D printer was invented in the 1980s, but it wasn't until the early 2000s that the technology became more accessible and affordable.
- The materials used in 3D printing include plastics, resins, metals, ceramics, and even food.
- 3D printers vary in size and capabilities, from small desktop printers for hobbyists to large industrial machines for manufacturing complex parts.
- The applications of 3D printing are vast, ranging from prototyping and product development to healthcare, aerospace, and even construction.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
To understand how 3D printing works, let's break it down into three main steps: design, slicing, and printing.
-
Design: The process begins with creating a digital 3D model using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software or by scanning an existing object using a 3D scanner. The design is then exported as a standard file format, such as .STL or .OBJ.
-
Slicing: The next step is to prepare the digital model for printing. Slicing software takes the 3D model and slices it into thin layers, generating a set of instructions for the 3D printer to follow. These instructions include parameters such as layer height, print speed, and material temperature.
-
Printing: Once the slicing process is complete, the file is transferred to the 3D printer. The printer heats the chosen material, such as plastic filament or liquid resin, to its melting or curing temperature. The material is then deposited layer by layer, following the instructions from the slicing software, until the object is fully formed.
Types of 3D Printers
There are several types of 3D printers available, each with its own unique technology and capabilities. Let's explore some of the most common types:
-
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM printers are the most popular and affordable type of 3D printers. They work by extruding a thermoplastic filament through a heated nozzle, which then solidifies to form the layers of the object. FDM printers are widely used in various industries and are great for beginners.
-
Stereolithography (SLA): SLA printers use a liquid resin that is cured by a UV laser or light source. The printer builds the object layer by layer by selectively curing the resin. SLA printers produce high-resolution prints with smooth surface finishes, making them ideal for detailed models and prototypes.
-
Digital Light Processing (DLP): DLP printers are similar to SLA printers but use a digital projector to cure the entire layer at once instead of a laser or light source. This results in faster print times but slightly lower resolution compared to SLA printers.
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS printers use a laser to selectively fuse powdered materials, such as nylon or metal, to create the object. The unused powder acts as support during the printing process, eliminating the need for additional support structures. SLS printers are commonly used for producing functional prototypes and end-use parts.
-
Metal 3D Printers: Metal 3D printers use various technologies, such as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) or Electron Beam Melting (EBM), to selectively melt metal powders and build metal objects layer by layer. These printers are primarily used in industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, where high-strength metal parts are required.
What Can You 3D Print?
The possibilities of 3D printing are virtually endless. Here are some common objects and applications that can be 3D printed:
-
Prototypes: 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping, enabling designers and engineers to quickly iterate and test their ideas before moving to mass production.
-
Customized Products: With 3D printing, it's possible to create personalized products tailored to individual needs, such as custom phone cases, jewelry, and even prosthetics.
-
Spare Parts: Instead of waiting for a replacement part to be shipped, 3D printing enables the on-demand production of spare parts, reducing downtime and costs.
-
Art and Sculptures: Artists and sculptors can use 3D printing to bring their creations to life with intricate details and complex geometries.
-
Medical Applications: 3D printing has revolutionized the medical field, allowing for the production of patient-specific implants, surgical guides, and even human organs.
-
Food: Yes, you can even 3D print food! Chefs and food enthusiasts have experimented with 3D printers to create intricate edible designs and customized chocolates.
How Do 3D Printers Work?
Now let's take a closer look at how a typical 3D printer works:
-
Preparation: Before printing, the 3D printer needs to be properly set up. This involves leveling the build plate, ensuring the nozzle or resin tank is clean, and loading the chosen material.
-
Heating: If using a filament-based printer, the printer heats the nozzle to the melting temperature of the filament. If using a resin-based printer, the printer prepares the resin by agitating it and heating it to the appropriate temperature.
-
Printing: The printer starts the printing process by depositing the first layer of material onto the build plate or in the resin tank. The printer then moves the print head or build platform according to the instructions from the slicing software, depositing subsequent layers until the object is complete.
-
Cooling and Finishing: Once the printing is finished, the object needs to cool and solidify. For filament-based printers, this happens naturally as the material cools down. For resin-based printers, the object is typically washed in a cleaning solution and then cured under UV light to fully harden.
The 3D Printing Process
To give you a better understanding of the 3D printing process, let's break it down into the following steps:
-
Design: Create a digital 3D model using CAD software or scan an existing object using a 3D scanner.
-
Slicing: Prepare the digital model for printing by slicing it into thin layers using slicing software.
-
Printing: Transfer the sliced file to the 3D printer and start the printing process. The printer follows the instructions from the slicing software, depositing material layer by layer to build the object.
-
Post-Processing: Once the printing is complete, remove the object from the printer and perform any necessary post-processing steps, such as removing support structures, sanding, or painting.
How Much Do 3D Printers Cost?
The cost of 3D printers can vary greatly depending on the type, size, and capabilities of the printer. Here is a general price range for different types of 3D printers:
-
Entry-Level FDM Printers: These printers are great for beginners and typically cost between $200 to $500. They offer basic functionality and are suitable for small-scale projects.
-
Mid-Range FDM Printers: These printers offer more advanced features and better print quality. Prices range from $500 to $2000.
-
High-End FDM Printers and Resin Printers: These printers are designed for professional use and can cost anywhere from $2000 to $10,000 or more. They offer higher precision, larger build volumes, and advanced features.
-
Industrial 3D Printers: These printers are used in large-scale manufacturing and can cost tens of thousands of dollars or more.
It's important to consider not only the upfront cost of the printer but also the ongoing costs of materials, maintenance, and upgrades.
3D Printing Examples
To illustrate the capabilities of 3D printing, let's explore some real-world examples:
-
Automotive Industry: 3D printing is used to produce prototypes, custom parts, and even entire cars. It enables faster design iterations and reduces the time and cost of traditional manufacturing processes.
-
Healthcare: Medical professionals use 3D printing to create patient-specific implants, prosthetics, surgical guides, and anatomical models for surgical planning.
-
Aerospace Industry: 3D printing is revolutionizing the aerospace industry by enabling the production of lightweight and complex parts. It also reduces material waste and allows for on-demand manufacturing.
-
Architecture and Construction: 3D printing is being explored as a way to construct buildings and structures more efficiently and sustainably. It has the potential to revolutionize the construction industry by reducing costs and waste.
-
Fashion and Jewelry: Designers are using 3D printing to create unique and intricate fashion pieces, accessories, and jewelry. It allows for complex geometries and customization.
3D Printing Uses
The applications of 3D printing are vast and continue to expand. Here are some of the key areas where 3D printing is being used:
-
Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing enables designers and engineers to quickly iterate and test their ideas before moving to mass production.
-
Custom Manufacturing: 3D printing allows for the production of customized products tailored to individual needs, from personalized phone cases to custom prosthetics.
-
Small-Batch Production: 3D printing is ideal for small-scale manufacturing, as it eliminates the need for expensive molds or tooling.
-
Tooling and Jigs: 3D printing is used to create custom tooling and jigs for various industries, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
-
Education and Research: 3D printing is widely used in educational settings to teach design and engineering concepts. It also plays a crucial role in scientific research and experimentation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing
Like any technology, 3D printing has its advantages and disadvantages. Let's take a closer look:
Advantages:
- Design Freedom: 3D printing allows for the creation of complex geometries and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to produce with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Customization: 3D printing enables the production of personalized products tailored to individual needs and preferences.
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing allows for quick iteration and testing of designs, reducing time and costs.
- Reduced Waste: 3D printing is an additive process, meaning it only uses the necessary amount of material, minimizing waste.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: 3D printing enables the production of parts and products on-demand, reducing inventory costs and lead times.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Material Selection: While the range of materials for 3D printing is expanding, it still lags behind traditional manufacturing methods in terms of material options.
- Print Speed: 3D printing can be a slow process, especially for larger and more complex objects.
- Post-Processing: Depending on the printing technology and material used, post-processing steps such as removing support structures or sanding may be required.
- Cost: While the cost of 3D printers has decreased over the years, high-quality printers and materials can still be expensive, especially for professional use.
FAQ

What is 3D printing in simple words?
3D printing is a manufacturing process that creates physical objects by depositing material layer by layer based on a digital design. It allows for the production of complex and customized objects that would be difficult or impossible to create with traditional manufacturing methods.
How does a 3D printer actually work?
A 3D printer works by melting or curing a material, such as plastic or resin, and precisely depositing it layer by layer to build a three-dimensional object. The process involves designing a digital model, slicing it into layers, and then printing each layer one by one.
What are 3D printers mainly used for?
3D printers are used in various industries and applications, including rapid prototyping, custom manufacturing, small-batch production, tooling and jigs, education, and research. They are also used in healthcare for creating patient-specific implants, prosthetics, and anatomical models.
Can a 3D printer print anything?
While 3D printers are versatile, there are limitations to what they can print. The choice of materials, size of the printer, and complexity of the design can all impact what can be printed. Additionally, some objects may require post-processing or assembly after printing.
Are 3D printers expensive?
The cost of 3D printers can vary greatly depending on the type, size, and capabilities of the printer. Entry-level printers can cost as low as a few hundred dollars, while high-end professional printers can cost tens of thousands of dollars or more.
Are 3D printers difficult to use?
While there may be a learning curve, many 3D printers are designed to be user-friendly, especially for beginners. However, more advanced features and settings may require some technical knowledge and experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printing is a groundbreaking technology that has revolutionized manufacturing, design, and various industries. It allows for the creation of complex, customized, and functional objects with incredible precision. From rapid prototyping to customized manufacturing, the possibilities of 3D printing are limitless. As the technology continues to advance and become more accessible, we can expect even more exciting applications and innovations in the future.
Thank you for joining us on this 3D printing journey! If you're interested in exploring the world of 3D printers further, check out our website Best 3D Printer™ for expert reviews, buying guides, and more.
Useful Links

- Shop 3D Printers on Amazon
- Shop 3D Printers on Walmart
- Shop 3D Printers on eBay
- 3D Printing Books on Amazon
Reference Links