Support our educational content for free when you purchase through links on our site. Learn more
The 3 Most Common Types of 3D Printers for [2023]

Welcome to another exciting blog post from the Best 3D Printer Awards™ team! Today, we are going to dive into the fascinating world of 3D printers and discuss the three most common types available. Whether you're a beginner looking to dip your toes into the world of 3D printing or a seasoned enthusiast seeking to expand your knowledge, this article is for you. So, without further ado, let's get started!
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- FAQ
- Quick Tips and Facts
- Useful Links
- Reference Links
Introduction
3D printing has revolutionized the manufacturing industry and brought the power of creation right to our fingertips. With a 3D printer, you can turn your digital designs into physical objects, opening up infinite possibilities. But before we dive into the types of 3D printers, let's quickly touch upon the concept of 3D printing itself.
At its core, 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that builds objects layer by layer, based on a digital model. The printer reads the model and deposits material, such as plastic or metal, to create the final product. This process allows for incredible design complexity and customization that traditional manufacturing methods cannot match.
Now that we have a basic understanding of 3D printing, let's explore the three most common types of 3D printers in more detail.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
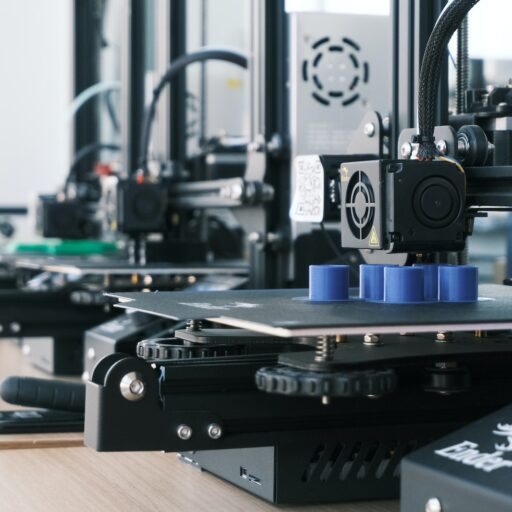
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is the most widely used and accessible 3D printing technology. It operates by extruding a continuous filament of thermoplastic material, such as PLA or ABS, through a heated nozzle. The filament is melted and deposited layer by layer onto a build platform, gradually building the object.
FDM printers are known for their affordability, ease of use, and versatility. They are widely used by hobbyists, educators, and small businesses for prototyping, customization, and even small-scale production. Some popular FDM printers include the Prusa i3 and the Creality Ender 3.
Benefits of FDM:
- Affordable and accessible
- Wide range of compatible materials
- User-friendly software and interface
- Large selection of FDM printers available in the market
Considerations for FDM:
- Lower printing resolution compared to other technologies
- Visible layer lines on the final print
- Limited suitability for intricate and detailed designs
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography (SLA) was one of the earliest 3D printing technologies and is still widely used today. It operates by using a liquid photopolymer resin that is cured layer by layer using an ultraviolet laser or light source. The resin solidifies upon exposure to light, creating the desired object.
SLA printers excel in producing high-resolution, smooth, and detailed objects. They are commonly used in industries such as jewelry, dentistry, and engineering, where precision is crucial. Some well-known SLA printers include the Formlabs Form 3 and the Anycubic Photon Mono X.
Benefits of SLA:
- Exceptional printing resolution and surface finish
- Ability to produce intricate and delicate designs
- Wide range of compatible resins available
- Suitable for small-scale production and professional use
Considerations for SLA:
- Higher cost of entry compared to FDM printers
- Limited selection of affordable SLA printers in the market
- Requires post-processing and additional safety precautions due to the use of liquid resin
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is an industrial-grade 3D printing technology that uses a high-powered laser to fuse powdered materials, such as nylon or metal, into a solid form. The powdered material is spread in a thin layer, and the laser selectively fuses the particles to create the desired shape.
SLS printers are renowned for their ability to produce complex geometric designs and functional parts with high durability. They are commonly used in manufacturing, aerospace, and automotive industries. Some notable SLS printers include the Formlabs Fuse 1 and the EOS P 396.
Benefits of SLS:
- Unparalleled design freedom for intricate and functional parts
- Excellent mechanical strength and durability
- Wide range of compatible materials, including nylon and metal
- Suitable for small-scale production and industrial applications
Considerations for SLS:
- High cost of equipment and materials
- Complex setup and operation
- Require specialized training and expertise
- Post-processing may be required to remove excess powder
FAQ
What are the most common types of 3D printers?
The most common types of 3D printers are Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). These technologies cater to a wide range of applications and user requirements.
What are the 3 main types of 2D printers called?
The three main types of 2D printers are laser printers, inkjet printers, and dot matrix printers. While they may seem similar on the surface, each type operates using a different printing process and has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Is SLS or FDM better?
The choice between SLS and FDM depends on your specific needs and budget. SLS offers unparalleled design freedom and durability but comes with a higher cost and complexity. FDM, on the other hand, is more affordable, easier to use, and suitable for a wide range of applications. Consider your requirements and budget before making a decision.
Quick Tips and Facts
- FDM is the most common and accessible type of 3D printer.
- SLA printers excel in producing high-resolution and detailed objects.
- SLS printers are known for their ability to create intricate and functional parts.
- Each type of printer uses different materials and processes to achieve the final result.
- When choosing a 3D printer, consider your budget, desired print quality, and intended applications.